Gold vs Fixed Deposits: Which is Best for Retirement Planning in India in 2024?
Table of Contents
Introduction
When planning for retirement, two of the most popular investment options are gold and fixed deposits (FDs). Both have their unique advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different financial goals and risk appetites. This article will explore the intricacies of these investment avenues, helping you make an informed decision on where to park your hard-earned money for a secure retirement.

Understanding Gold as an Investment
Types of Gold Investments
| Type of Gold Investment | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Gold | Includes gold jewellery, coins, and bars. |
| Gold ETFs | Exchange-traded funds that invest in gold. |
| Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs) | Issued by the Government of India, offering interest payments. |
Historical Performance of Gold
Gold has been considered a safe-haven asset, especially during economic downturns. Historically, gold prices have shown a steady increase, particularly during periods of inflation or geopolitical instability. In the last decade, gold has delivered an average annual return of around 8-10%.
Pros and Cons of Investing in Gold
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Hedge Against Inflation | Storage and Security Issues |
| High Liquidity | No Regular Income |
| Diversification Benefits | Short-Term Price Volatility |
Understanding Fixed Deposits (FDs)
Types of Fixed Deposits
| Type of Fixed Deposit | Description |
|---|---|
| Bank FDs | Offered by banks with fixed interest rates for specific tenures. |
| Corporate FDs | Offered by NBFCs with higher interest rates but higher risk. |
Historical Performance of FDs
Fixed deposits have been a preferred investment for risk-averse individuals due to their guaranteed returns and safety. Historically, bank FDs have offered interest rates ranging from 5% to 7% per annum.
Pros and Cons of Investing in FDs
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| High Safety | Inflation Risk |
| Regular Income | Liquidity Issues |
| Fixed and Guaranteed Returns | Lower Returns Compared to Other Assets |
Gold vs Fixed Deposits: Key Comparisons
Risk and Stability
| Factor | Gold | Fixed Deposits |
|---|---|---|
| Risk | Higher due to price volatility | Lower, stable and guaranteed returns |
| Stability | Acts as a hedge against economic downturns | Highly stable, ideal for risk-averse investors |
Returns on Investment
| Factor | Gold | Fixed Deposits |
|---|---|---|
| Long-Term Returns | Historically higher | Steady but lower |
| Short-Term Volatility | High | Low |
Liquidity and Accessibility
| Factor | Gold | Fixed Deposits |
|---|---|---|
| Liquidity | Highly liquid | Liquid but with penalties on early withdrawal |
| Accessibility | Easily bought and sold | Easily accessible but with fixed tenure |
Tax Implications
| Factor | Gold | Fixed Deposits |
|---|---|---|
| Taxation | Long-term capital gains are taxed at 20% with indexation | Interest taxed as per income slab |
| Tax Benefits | Indexation benefits reduce tax liability | No special tax benefits |
Inflation Hedge: Gold vs FDs
| Factor | Gold | Fixed Deposits |
|---|---|---|
| Inflation Protection | Excellent hedge against inflation | May not keep up with inflation |
Security and Safety
| Factor | Gold | Fixed Deposits |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Security | Requires secure storage | Insured up to ₹5 lakh by DICGC |
| Institutional Safety | SGBs and ETFs mitigate physical risks | High due to regulatory protections |
Impact of Economic Conditions
| Factor | Gold | Fixed Deposits |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Downturns | Performs well during downturns | Less affected, provides steady returns |
| Interest Rate Impact | Less directly affected | Directly affected by interest rate changes |
Flexibility and Accessibility
| Factor | Gold | Fixed Deposits |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Flexibility | Flexible with various forms | Fixed tenure, penalties for premature withdrawal |
| Loan Facility | Loans available against gold | Loans available against FDs |
Tax considerations
| Factor | Gold | Fixed Deposits |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Taxation | Not applicable for physical gold, SGBs have interest-taxed | Interest fully taxable |
| Capital Gains | Long-term gains taxed at 20% with indexation | Not applicable |
Long-Term Growth Potential
Gold has shown significant long-term growth potential, especially during periods of economic instability. FDs offer steady but lower growth, making them suitable for conservative investors looking for guaranteed returns.
Case Studies and Example
Gold Investments for Retirement
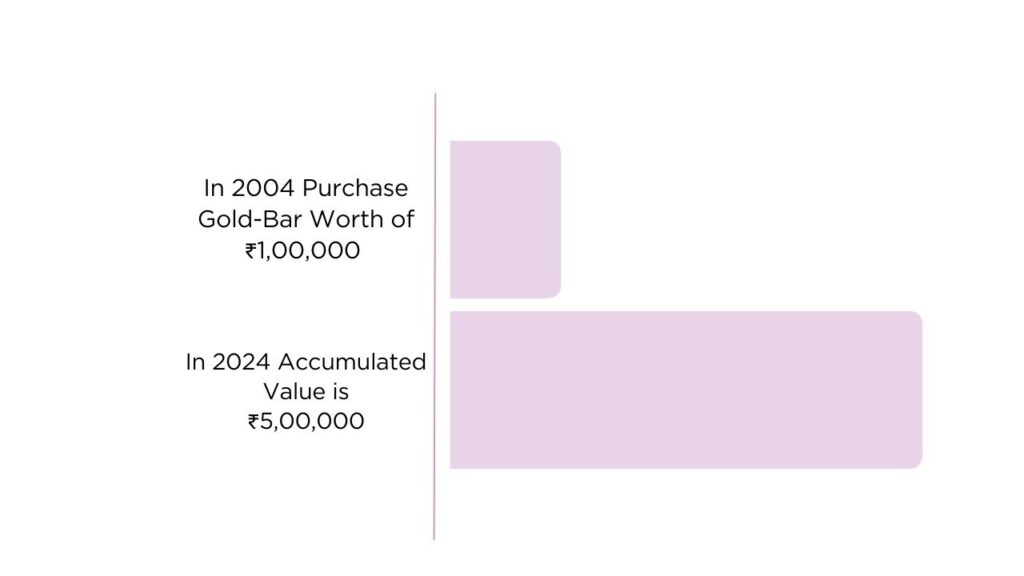
Consider an individual who invested in gold 20 years ago. Let’s say they purchased gold bars worth ₹1,00,000 in the year 2004. Over the next two decades, despite short-term volatility, the value of gold has appreciated significantly. As of 2024, the value of the same gold bars is estimated to be around ₹5,00,000, representing a fivefold increase in value. This example illustrates the long-term growth potential of gold as an investment, serving as a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainties.
FD Investments for Retirement
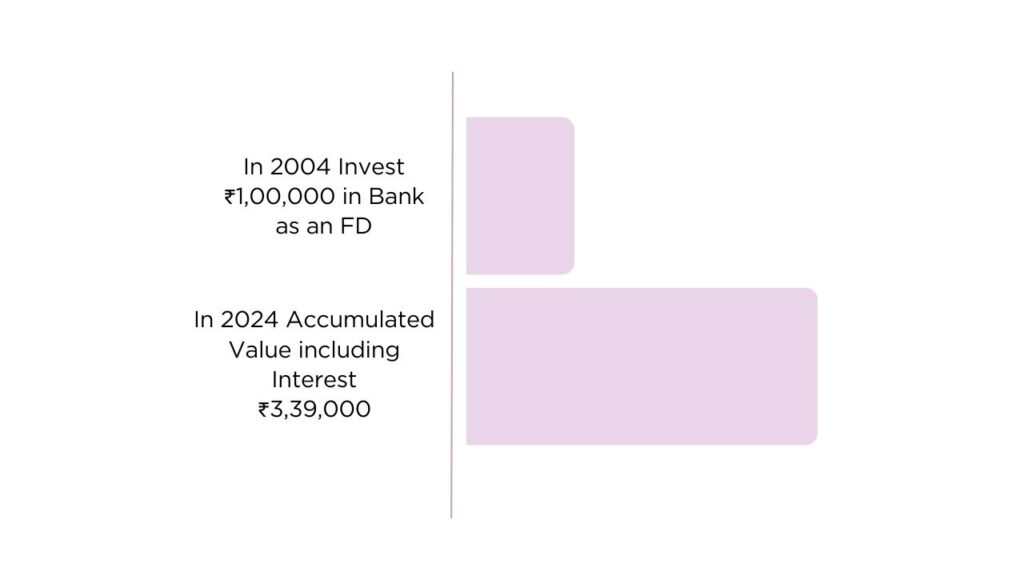
Now, let’s look at an individual who invested in fixed deposits 20 years ago. Suppose they deposited ₹1,00,000 in a bank FD in 2004, earning an annual interest rate of 7%. Over the next two decades, the FD would have matured, and the accumulated value, including interest, would be approximately ₹3,39,000. While FDs offer safety and guaranteed returns, the real value of the returns may have been eroded by inflation over time. This example highlights the steady but relatively lower growth of fixed deposits compared to other investment options like gold.
Diversification Strategies: Combining Gold and Fixed Deposits
One effective way to balance risk and returns in your retirement portfolio is to combine both gold and fixed deposits. This strategy leverages the strengths of both assets, providing a hedge against inflation while ensuring capital protection.
Diversification Strategies: Combining Gold and Fixed Deposits
- Risk Management: By diversifying, you reduce the risk of significant losses. If one asset underperforms, the other might compensate, leading to a more stable overall return.
- Balanced Growth: While gold can provide capital appreciation during market uncertainties, FDs offer steady income, creating a balanced growth portfolio.
Scenario Analysis:
- During High Inflation: Gold typically outperforms during periods of high inflation as it is seen as a haven. In such scenarios, the value of FDs may erode if the interest rates do not keep pace with inflation.
- In a Stable Economy: Fixed deposits may perform better in a stable economy with low inflation, where the returns from FDs provide a reliable income stream, while gold may offer modest gains or even depreciate.
Economic Factors and Global Events: Impact on Gold and Fixed Deposits
Global economic events and domestic policies play a crucial role in determining the performance of both gold and fixed deposits. Understanding these factors can help you make informed investment decisions.
Global Economic Events:
- Recessions: During recessions, central banks often lower interest rates to stimulate the economy. This can lead to lower returns on FDs, while gold prices may rise as investors seek safer assets.
- Trade Wars: Trade tensions can lead to economic uncertainty, pushing up gold prices as a hedge against potential losses in other markets. Meanwhile, FDs might offer lower interest rates during such periods.
- Pandemics: The COVID-19 pandemic is a recent example of how global crises can impact investments. Gold prices surged as investors flocked to safe-haven assets, while interest rates on FDs dropped to historic lows.
Inflation vs. Interest Rates:
- Inflation Impact on Gold: Gold is often considered an effective hedge against inflation. When inflation rises, the real value of paper currency decreases, but gold tends to retain or increase its value.
- Inflation Impact on FDs: Fixed deposits, on the other hand, may suffer during high inflation if the interest rates on FDs are lower than the inflation rate. This can result in negative real returns, diminishing the purchasing power of your savings.
Alternatives to Gold and Fixed Deposits
Mutual Funds:
While gold and FDs are popular, other investment options may also be worth considering for a well-rounded retirement plan.
- Risk and Return: Mutual funds offer the potential for higher returns than FDs and gold, but they come with higher risk, particularly equity mutual funds.
- Tax Efficiency: Long-term capital gains from equity mutual funds are taxed at a lower rate compared to the interest on FDs.
Real Estate:
- Tangible Asset: Like gold, real estate is a tangible asset that can provide both capital appreciation and rental income.
- Liquidity Concerns: However, real estate is less liquid than gold and FDs, making it more challenging to sell quickly in times of need.
Stocks:
- Growth Potential: Investing in stocks offers high growth potential but also comes with higher volatility and risk.
Dividend Income:
Some stocks offer dividends, providing a regular income stream similar to FDs.
Case Studies and Historical Data: Learning from the Past
Examining past performance can provide valuable insights into how gold and fixed deposits might perform in the future.
Case Study 1: The 2008 Financial Crisis
- Gold Performance: During the 2008 financial crisis, gold prices soared as investors fled to safe-haven assets, providing substantial returns to those who held gold.
- FD Performance: Interest rates on fixed deposits fell during the crisis as central banks slashed rates to stimulate the economy, leading to lower returns for FD holders.
Case Study 2: Post-Pandemic Recovery
- Gold Performance: In the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, gold prices initially surged but later stabilized as economies began to recover.
- FD Performance: Interest rates on FDs remained low due to central banks’ accommodative policies, offering modest returns.
Future Outlook: What Lies Ahead for Gold and FDs?
Looking to the future, both gold and fixed deposits will continue to play vital roles in retirement planning. However, staying informed about economic trends and adjusting your investment strategy accordingly will be crucial.
Economic Predictions:
- Gold: Analysts predict that gold will continue to be an asset, especially as global uncertainties and inflation concerns persist.
- FDs: Fixed deposit rates may remain low in the short term, but they are expected to gradually rise as central banks adjust their monetary policies.
Interactive Tools and Calculators: Plan Your Retirement
Utilizing online tools can help you visualize how different investment strategies might impact your retirement savings.
Retirement Calculator:
- Personalized Planning: Use an interactive retirement calculator to input your age, financial goals, and risk tolerance. This tool can help you determine the ideal mix of gold and FDs for your retirement plan.
Gold vs FD Growth Simulator:
- Simulation Tool: Try a growth simulator to see how your investment in gold and FDs could grow over time. Adjust variables like inflation, interest rates, and market conditions to see how they affect your returns.
Conclusion
In the end, the choice between gold and fixed deposits—or a combination of both—depends on your circumstances, financial goals, and risk tolerance. By understanding the pros and cons of each option and considering the broader economic context, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your retirement aspirations.
Whether you opt for the historical stability of gold or the assured returns of fixed deposits, the key is to create a balanced portfolio that secures your financial future and provides peace of mind during your golden years.
